Table Of Content
Longitudinal research design is used to study changes in a particular phenomenon over time. It involves collecting data at multiple time points and analyzing the changes that occur. The aim of longitudinal research is to provide insights into the development, growth, or decline of a particular phenomenon over time.
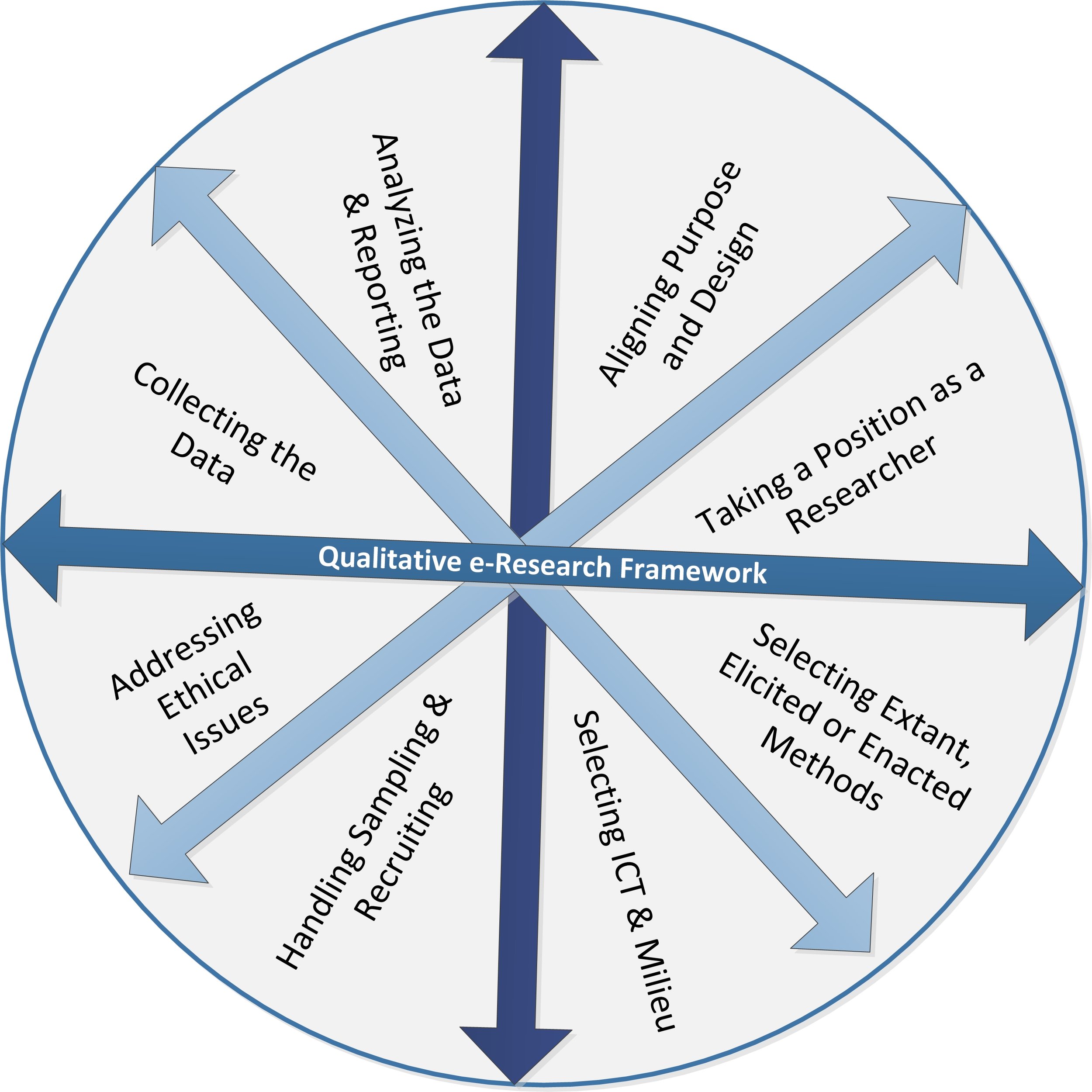
Case selection in qualitative research
Overall, an appropriately chosen and executed research design helps researchers to conduct high-quality research, draw meaningful conclusions, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field. Broadly, research design types can be divided into qualitative and quantitative research. A research design is essential to systematically investigate, understand, and interpret phenomena of interest.
What Are the Different Types of Research Design?
When creating your research design, consider your overall objectives, how you plan to sample, and how you intend to collect and analyze your data. Determine which methods are the most appropriate for the research you’ll be doing. Causal research works to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables. Many companies use this research design to determine the impact a change in a product or process will make.
Frequently asked questions

Construct validity examines how well a given measurement scale is measuring the theoretical construct that it is expected to measure. Many constructs used in social science research such as empathy, resistance to change, and organisational learning are difficult to define, much less measure. For instance, construct validity must ensure that a measure of empathy is indeed measuring empathy and not compassion, which may be difficult since these constructs are somewhat similar in meaning. Construct validity is assessed in positivist research based on correlational or factor analysis of pilot test data, as described in the next chapter. Mixed-Methods ExampleAn education researcher interested in student motivation might use a mixed-method approach.
In statistical control, extraneous variables are measured and used as covariates during the statistical testing process. Systematic Review ExampleA health researcher interested in the impact of a plant-based diet on heart disease might conduct a systematic review of all published studies on the topic. They would gather, analyze, and synthesize data from these studies to draw a comprehensive understanding of the current evidence base on this issue.
What are the different types of research design?
Sometimes, people get so wrapped up in the details that they can lose sight of the goal. This type of research has numerous applications, and several industries use it. It can deliver a high level of evidence based on the research and determine cause and effect in many situations. In descriptive research design, the intent is to describe a situation or case by systematically obtaining data to describe the phenomenon, population, or event.
Meet the Methods Series: Quantitative intersectional study design and primary data collection - Instituts de recherche en santé du Canada
Meet the Methods Series: Quantitative intersectional study design and primary data collection.
Posted: Wed, 04 Aug 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Specifically, we’ll look at phenomenological design, grounded theory design, ethnographic design, and case study design. This means that the researcher needs to assign participants to different groups or conditions in a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to any group (note that this is not the same as random sampling). For example, withholding a potentially beneficial medical treatment from a control group may be considered unethical in certain situations. We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version.
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”. This type of research is quite contrary to the quantitative research design.
They would likely examine a variety of texts, historical contexts, and moral frameworks, before formulating a comprehensive theory of justice. Field research is a qualitative method of research concerned with understanding and interpreting the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within a specific social or environmental setting. Historical Research Example A historian might conduct research on the economic impact of the Great Depression on the United States. They would likely analyze data from that era, such as economic indicators, governmental policies, and personal accounts to form a comprehensive understanding of the economic climate of the time. “systematic collection and analysis of data for the purpose of taking action and making change” (p.264). Exploratory Research Example DesignConsider a business that is noticing a decline in its customer retention rates.
Brand24, a social listening tool, tripled its sign-up conversion rate from 2.56% to 7.42%, thanks to locating friction points in the sign-up form through screen recordings. Descriptive research refers to a systematic process of observing and describing what a subject does without influencing them. Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups. It’s also important to create a data management plan for organising and storing your data. For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
Qualitative research is subjective and exploratory; it determines relationships between collected data and observations. It is usually carried out through interviews with open-ended questions, observations that are described in words, etc. Quantitative research, on the other hand, is more objective and employs statistical approaches.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students. As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method, you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample. Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population. As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics.
As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information). Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire.

No comments:
Post a Comment